| THERE WAS AT THIS SAME TIME in Florence a painter of most beautiful intelligence and most lovely invention, namely, Filippo, son of Fra Filippo of the Carmine, who, following in the steps of his dead father in the art of painting, was brought up and instructed, being still very young, by Sandro Botticelli, notwithstanding that his father had com- mended him on his deathbed to Fra Diamante, who was much his friend nay, almost his brother. Such was the intelligence of Filippo, and so abundant his invention in painting, and so bizarre and new were his ornaments, that he was the first who showed to the moderns the new method of giving variety to vestments, and embellished and adorned his figures with the girt-up garments of antiquity. He was also the first to bring to light grotesques, in imitation of the antique, and he executed them on friezes in terretta or in colors, with more design and grace than the men before him had shown; wherefore it was a marvellous thing to see the strange fancies that he expressed in painting. What is more, he never executed a single work in which he did not avail himself with great diligence of Roman antiquities, such as vases, buskins, trophies, banners, helmet-crests, adornments of temples, ornamental head-dresses, strange kinds of draperies, armor, scimitars, swords, togas, mantles, and such a variety of other beautiful things, that we owe him a very great and perpetual obligation, seeing that he added beauty and adornment to art in this respect.
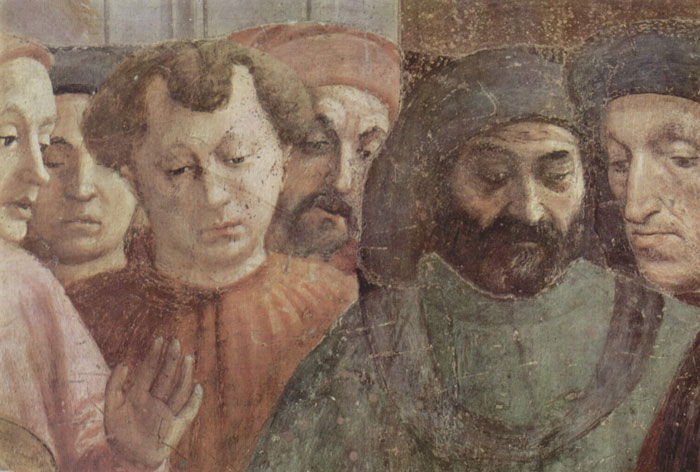
In his earliest youth he completed the Chapel of the Brancacci in the Carmine at Florence, begun by Masolino, and left not wholly finished by Masaccio on account of his death. Filippo, therefore, gave it its final perfection with his own hand, and executed what was lacking in one scene, wherein S. Peter and S. Paul are restoring to life the nephew of the Emperor. In the nude figure of this boy he portrayed the painter Francesco Granacci, then a youth; and he also made portraits of the Chevalier, Messer Tommaso Soderini, Piero Guicciardini, father of Messer Francesco the historian, Piero del Pugliese, and the poet Luigi Pulci; likewise Antonio Pollaiuolo, and himself as a youth, as he then was, which he never did again throughout the whole of his life, so that it has not been possible to find a portrait of him at a more mature age. In the scene following this he portrayed Sandro Botticelli, his master, and many other friends and people of importance; among others, the broker Raggio, a man of great intelligence and wit, who executed in relief on a conch the whole Inferno of Dante, with all the circles and divisions of the pits and the nethermost well in their exact proportions, and all the figures and details that were most ingeniously imagined and described by that great poet; which conch was held in those times to be a marvellous thing.
Next, in the Chapel of Francesco del Pugliese at Campora, a seat of the Monks of the Badia, without Florence, he painted a panel in distemper of S. Bernard, to whom Our Lady is appearing with certain angels, while he is writing in a wood; which picture is held to be admirable in certain, respects, such as rocks, books, herbage, and similar things, that he painted therein, besides the portrait from life of Francesco himself, so excellent that he seems to lack nothing save speech. This panel was removed from that place on account of the siege, and placed for safety in the Sacristy of the Badia of Florence. In S. Spirito in the same city, for Tanai de' Nerli, he painted a panel with Our Lady, S. Martin, S. Nicholas, and S. Catherine; with a panel in the Chapel of the Rucellai in S. Pancrazio, and a Crucifix and two figures on a ground of gold in S. Raffaello. In front of the Sacristy of S. Francesco, without the Porta a S. Miniato, he made a God the Father, with a number of children. At Palco, a seat of the Frati del Zoccolo, without Prato, he painted a panel; and in the Audience Chamber of the Priori in that territory he executed a little panel containing the Madonna, S. Stephen, and S. John the Baptist, which has been much extolled. On the Canto al Mercatale, also in Prato, in a shrine opposite to the Nuns of S. Margherita, and near some houses belonging to them, he painted in fresco a very beautiful Madonna, with a choir of seraphim, on a ground of dazzling light. In this work, among other things, he showed art and beautiful judgment in a dragon that is at the feet of S. Margaret, which is so strange and horrible, that it is revealed to us as a true fount of venom, fire, and death; and the whole of the rest of the work is so fresh and vivacious in colouring, that it deserves infinite praise.
He also wrought certain things in Lucca, particularly a panel in a chapel of the Church of S. Ponziano, which belongs to the Monks of Monte Oliveto; in the centre of which chapel there is a niche containing a very beautiful S. Anthony in relief by the hand of Andrea Sansovino, a most excellent sculptor. Being invited to go to Hungary by King Matthias, Filippo refused, but made up for this by painting two very beautiful panels for that King in Florence, and sending them to him; and in one of these he made a portrait of the King, taken from his likeness on medals. He also sent certain works to Genoa; and beside the Chapel of the High Altar in S. Domenico at Bologna, on the left hand, he painted a S. Sebastian on a panel, which was a thing worthy of much praise. For Tanai de' Nerli he executed another panel in S. Salvadore, without Florence; and for his friend Piero del Pugliese he painted a scene with little figures, executed with so much art and diligence that when another citizen besought him to make a second like it, he refused, saying that it was not possible to do it.
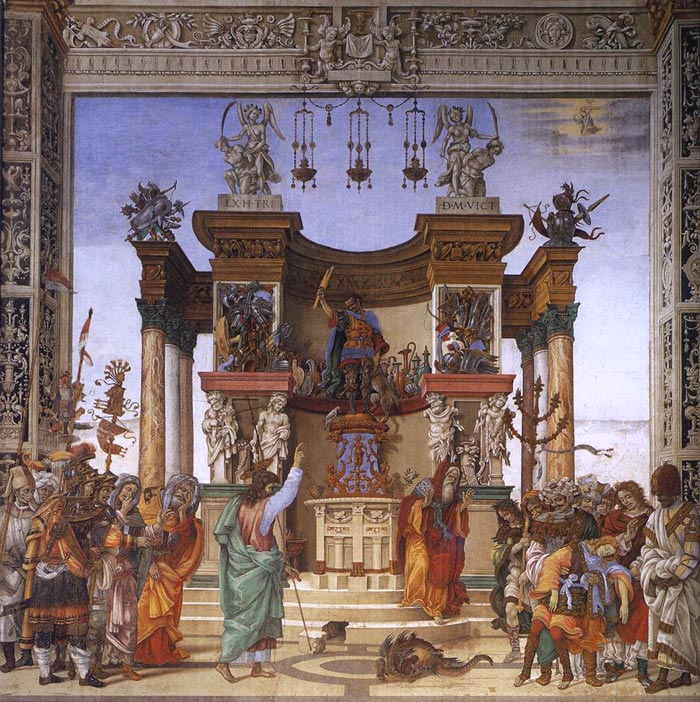
After these things he executed a very great work in Rome for the Neapolitan Cardinal, Olivieri Caraffa, at the request of the elder Lorenzo de' Medici, who was a friend of that Cardinal. While going thither for that purpose, he passed through Spoleto at the wish of Lorenzo, in order to give directions for the making of a marble tomb for his father Fra Filippo at the expense of Lorenzo, who had not been able to obtain his body from the people of Spoleto for removal to Florence. Filippo, therefore, made a beautiful design for the said tomb, and Lorenzo had it erected after that design (as has been told in another place), sumptuous and beautiful. Afterwards, having arrived in Rome, Filippo painted a chapel in the Church of the Minerva for the said Cardinal Caraffa, depicting therein scenes from the life of S. Thomas Aquinas, and certain most beautiful poetical compositions ingeniously imagined by himself, for he had a nature ever inclined to this. In the scene, then, wherein Faith has taken Infidelity captive, there are all the heretics and infidels. Hope has likewise overcome Despair, and so, too, there are many other Virtues that have subjugated the Vice that is their opposite. In a disputation is S. Thomas defending the Church "ex cathedra" against a school of heretics, and holding vanquished beneath him Sabellius, Arius, Averroes, and others, all clothed in graceful garments ; of which scene we have in our book of drawings the original design by Filippo's own hand, with certain others by the same man, wrought with such mastery that they could not be bettered. There, too, is the scene when, as S. Thomas is praying, the Crucifix says to him, "Bene scripsisti de me, Thoma "; while a companion of the Saint, hearing that Crucifix thus speaking, is standing amazed and almost beside himself. In the panel is the Virgin receiving the Annunciation from Gabriel; and on the main wall there is her Assumption into Heaven, with the twelve Apostles round the sepulchre. The whole of this work was held, as it still is, to be very excellent and wrought perfectly for a work in fresco. It con- tains a portrait from life of the said Cardinal Olivieri Caraffa, Bishop of Ostia, who was buried in this chapel in the year 1511, and afterwards removed to the Piscopio in Naples.
Having returned to Florence, Filippo undertook to paint at his leisure the Chapel of the elder Filippo Strozzi in S. Maria Novella, and he actually began it; but, having finished the ceiling, he was compelled to return to Rome, where he wrought a tomb with stucco work for the said Cardinal, and decorated with gesso a little chapel beside that tomb in a part of the same Church of the Minerva, together with certain figures, some of which were executed by his disciple, Raffaellino del Garbo. The chapel described above was valued by Maestro Lanzilago of Padua and by the Roman Antonio, known as Antoniasso, two of the best painters that were then in Rome, at 2,000 ducats of gold, without the cost of the blues and of the assistants. Having received this sum, Filippo returned to Florence, where he finished the aforesaid Chapel of the Strozzi, which was executed so well, and with so much art and design, that it causes all who see it to marvel, by reason of the novelty and variety of the bizarre things that are seen therein armed men, temples, vases, helmet crests, armor, trophies, spears, banners, garments, buskins, headdresses, sacerdotal vestments, and other things all executed in so beautiful a manner that they deserve the highest commendation. In this work there is the scene of Drusiana being restored to life by S. John the Evangelist, wherein we see most admirably expressed the marvel of the bystanders at beholding a man restore life to a dead woman by a mere sign of the cross; and the greatest amazement of all is seen in a priest, or rather philosopher, whichever he may be, who is clothed in ancient fashion and has a vase in his hand. In the same scene, likewise, among a number of women draped in various manners, there is a little boy, who, terrified by a small spaniel spotted with red, which has seized him with its teeth by one of his swathingbands, is running round his mother and hiding himself among her clothes, and appears to be as much afraid of being bitten by the dog as his mother is awestruck and filled with a certain horror at the resurrection of Drusiana. Next to this, in the scene where S. John himself is being boiled in oil, we see the wrath of the judge, who is giving orders for the fire to be increased, and the flames reflected on the face of the man who is blowing at them; and all the figures are painted in beautiful and varied attitudes.
On the other side is S. Philip in the Temple of Mars, compelling the serpent, which has slain the son of the King with its stench, to come forth from below the altar. In certain steps the painter depicted the hole through which the serpent issued from beneath the altar, and so well did he paint the cleft in one of the steps, that one evening one of Filippo's lads, wishing to hide something, I know not what, from the sight of someone who was knocking for admittance, ran up in haste in order to conceal it in the hole, being wholly deceived by it. Filippo also showed so much art in the serpent, that its venom, fetid breath, and fire, appear rather real than painted. Greatly extolled, too, is his invention in the scene of the Crucifixion of that Saint, for he imagined to himself, so it appears, that the Saint was stretched on the cross while it lay on the ground, and that ropes and cords are wound round certain fragments of antiquities, pieces of pillars, and bases, and pulled by certain ministers. On the other side the weight of the said cross and of the Saint who is stretched nude thereon is supported by two men, on the one hand by a man with a ladder, with which he is propping it up, and on the other hand by another with a pole, upholding it, while two others, setting a lever against the base and stem of the cross, are balancing its weight and seeking to place it in the hole made in the ground, wherein it had to stand upright. But why say more? It would not be possible for the work to be better either in invention or in drawing, or in any other respect whatsoever of industry or art. Besides this, it contains many grotesques and other things wrought in chiaroscuro to resemble marble, executed in strange fashion with invention and most beautiful drawing.
For the Frati Scopetini, also, at S. Donate, without Florence, which is called Scopeto and is now in ruins, he painted a panel with the Magi presenting their offerings to Christ, finished with great diligence, wherein he portrayed the elder Pier Francesco de' Medici, son of Lorenzo di Bicci, in the figure of an astrologer who is holding a quadrant in his hand, and likewise Giovanni, father of Signer Giovanni de' Medici, and another Pier Francesco, brother of that Signer Giovanni, and other people of distinction. In this work are Moors, Indians, costumes of strange shapes, and a most bizarre hut. In a loggia at Poggio a Cajano he began a Sacrifice in fresco for Lorenzo de' Medici, but it remained unfinished. And for the Nunnery of S. Geronimo, above the Costa di S. Giorgio in Florence, he began the panel of the high altar, which was brought nearly to completion after his death by the Spaniard Alonzo Berughetta, but afterwards wholly finished by other painters, Alonzo having gone to Spain. In the Palazzo della Signoria he painted the panel of the hall where the Council of Eight held their sittings, and he made the design for another large panel, with its ornament, for the Sala del Consiglio; which design his death prevented him from beginning to put into execution, although the ornament was carved; which ornament is now in the possession of Maestro Baccio Baldini, a most excellent physician of Florence, and a lover of every sort of talent. For the Church of the Badia of Florence he made a very beautiful S. Jerome; and he began a Deposition from the Cross for the high altar of the Friars of the Nunziata, but only finished the figures in the upper half of the picture, for, being overcome by a most cruel fever and by that contraction of the throat that is commonly known as quinsy, he died in a few days at the age of forty-five.
Thereupon, having ever been courteous, affable, and kindly, he was lamented by all those who had known him, and particularly by the youth of his noble native city, who, in their public festivals, masques, and other spectacles, ever availed themselves, to their great satisfaction, of the ingenuity and invention of Filippo, who has never had an equal in things of that kind. Nay, he was so excellent in all his actions, that he blotted out the stain (if stain it was) left to him by his father blotted it out, I say, not only by the excellence of his art, wherein he was inferior to no man of his time, but also by the modesty and regularity of his life, and, above all, by his courtesy and amiability ; and how great are the force and power of such qualities to conciliate the minds of all men without exception, is only known to those who either have experienced or are experiencing it. Filippo was buried by his sons in S. Michele Bisdomini [Visdomini] , on April 13, 1505; and while he was being borne to his tomb all the shops in the Via de' Servi were closed, as is done sometimes for the obsequies of great men.
Among the disciples of Filippo, who all failed by a great measure to equal him, was Raffaellino del Garbo, who made many works, as will be told in the proper place, although he did not justify the opinions and hopes that were conceived of him while Filippo was alive and Raffaellino himself still a young man. The fruits, indeed, are not always equal to the blossoms that are seen in the spring. Nor did any great success come to Niccolo Zoccolo, otherwise known as Niccolo Cartoni, who was likewise a disciple of Filippo, and painted at Arezzo the wall that is over the altar of S. Giovanni Decollate; a little panel, passing well done, in S. Agnesa; a panel over a lavatory in the Abbey of S. Fiora, containing a Christ who is asking for water from the woman of Samaria; and many other works, which, since they were commonplace, are not mentioned.
|
|

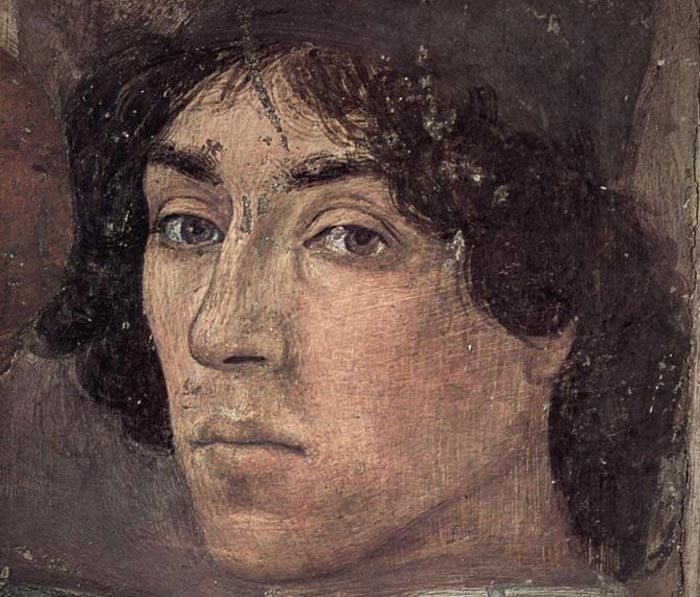
 Filippino Lippi (attr.), Self-Portrait (detail) Filippino Lippi (attr.), Self-Portrait (detail)
Detached fresco on flat tile, 50 x 31 cm
Galleria degli Uffizi, Florence

Self-Portrait [dice Vasari]. Detail from the Disputation with Simon Magus and Crucifixion of Peter.
1481-1482. Fresco. Brancacci Chapel, Santa Maria del Carmine, Florence.
|